What Foreign Objects Might Be Left in Patients After Surgery?
Some surgical tools and instruments that could be mistakenly left inside a surgical patient after the procedure is complete include the following:
 Clamps — Clamps are one of the most commonly used tools in surgical procedures. They can block blood flow through an artery or vein to prevent internal bleeding. They also move tissue out of the way so the surgeon can more easily see what’s happening during a procedure.
Clamps — Clamps are one of the most commonly used tools in surgical procedures. They can block blood flow through an artery or vein to prevent internal bleeding. They also move tissue out of the way so the surgeon can more easily see what’s happening during a procedure.
 Cotton swabs — Cotton swabs are often used to clean an incision site during or after surgery. If left inside a patient’s body, they also can become infected or interfere with normal bodily functions.
Cotton swabs — Cotton swabs are often used to clean an incision site during or after surgery. If left inside a patient’s body, they also can become infected or interfere with normal bodily functions.
 Gauze pads — Gauze pads are another tool to clean an incision site during or after surgery. Medical professionals also use them to soak up blood or fluids during the procedure. Gauze left after surgery can quickly become infected, leading to additional complications.
Gauze pads — Gauze pads are another tool to clean an incision site during or after surgery. Medical professionals also use them to soak up blood or fluids during the procedure. Gauze left after surgery can quickly become infected, leading to additional complications.
 Sponges — Surgical sponges are another implement used to clean incision sites and soak bodily fluids. Like cotton swabs and gauze pads, sponges left inside a patient can become infected.
Sponges — Surgical sponges are another implement used to clean incision sites and soak bodily fluids. Like cotton swabs and gauze pads, sponges left inside a patient can become infected.
 Needles — Needles used to place sutures inside a surgical patient are some of the most dangerous implements left inside the body. These needles can puncture organs and other tissues because they are sharp, causing severe internal bleeding and other complications.
Needles — Needles used to place sutures inside a surgical patient are some of the most dangerous implements left inside the body. These needles can puncture organs and other tissues because they are sharp, causing severe internal bleeding and other complications.
 Scissors — Surgical scissors are another of the most dangerous objects that might be left inside a surgical patient. Scissors are much bigger than needles and have multiple sharp edges, which can cause even more damage.
Scissors — Surgical scissors are another of the most dangerous objects that might be left inside a surgical patient. Scissors are much bigger than needles and have multiple sharp edges, which can cause even more damage.
 Catheters — Catheters are thin, flexible tubes used to either drain fluid from your body or add fluid to it. A catheter left inside a surgical patient can significantly interfere with the patient’s bodily functions or become infected.
Catheters — Catheters are thin, flexible tubes used to either drain fluid from your body or add fluid to it. A catheter left inside a surgical patient can significantly interfere with the patient’s bodily functions or become infected.
What Symptoms Does a Foreign Object Left in a Patient’s Body After Surgery Cause?
There are a few symptoms to look out for after surgery to make sure you’re healing properly. Common symptoms from foreign objects left in the body after surgery include the following:
- A mass inside the body at or near the surgical incision
- A high fever
- Discoloration around the incision site
- The incision site oozes blood, pus, or other fluids
- The incision site feels swollen or hard
- Stitches at the incision site start to pull apart
- Difficulty urinating or with bowel movements
- Pain or fatigue that becomes worse over time
- Vomiting or coughing up blood
- Difficulty breathing
- Bad odor coming from the incision site
You should contact your doctor immediately if you have any of these symptoms.
What to Do if You’re a Victim of Unintended Retention of Foreign Objects
You could take some actions to help you recover physically and financially if a surgical tool was left in your body. Here are the steps to take if you have a foreign object left inside you after surgery:
- Find a new doctor — Your prior doctor and the facility where the surgery was performed may try to avoid taking responsibility for a retained foreign object. See a new doctor and get the treatment you need.
- Gather your medical records — Find all your documents related to the initial surgery, so an attorney can determine what went wrong and who may be liable for your injuries.
- Contact a medical malpractice attorney — Having a foreign object left inside you after surgery is a major medical mistake. You deserve a chance to pursue compensation for the pain caused by the medical team’s negligence. An experienced medical malpractice lawyer can help you pursue compensation for your foreign body left after surgery.
What Damages Can Be Recovered from a Medical Malpractice Lawsuit?
If you have had a foreign object left inside you after surgery, a medical malpractice lawyer can help you seek compensation for:
- The cost of additional surgeries or other treatment you may need
- The pain and suffering from your injuries
- Any emotional distress caused by your injuries
- Lost income while you recover from your injuries
- Reduced future earnings due to a disability caused by the medical error
Surgeons and other healthcare providers could be held accountable if they leave foreign objects inside patients after surgery. If you have been the victim of surgical malpractice in Georgia, contact Geiger Legal Group, LLC, to speak with one of our experienced medical malpractice lawyers during a free and confidential consultation.
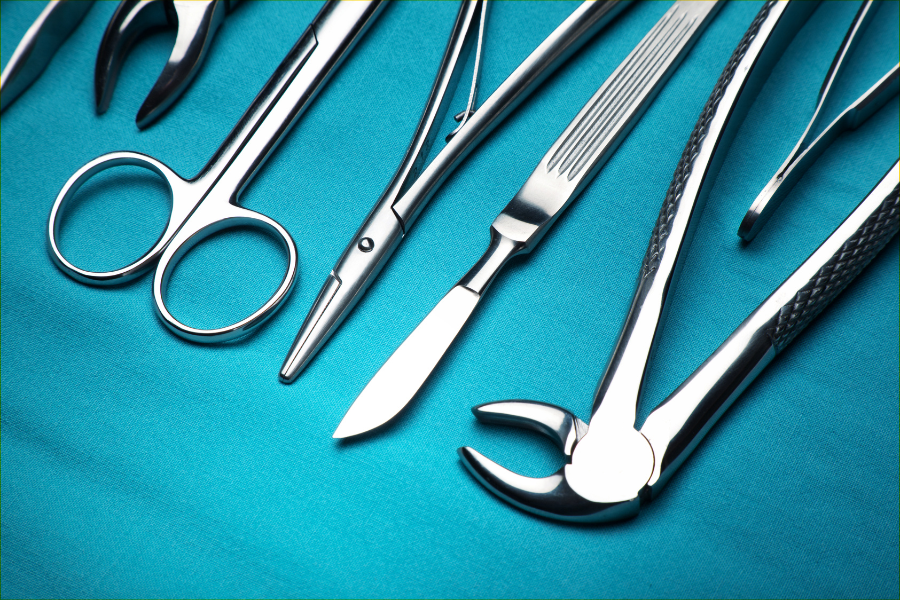



 Clamps — Clamps are one of the most commonly used tools in surgical procedures. They can block blood flow through an artery or vein to prevent internal bleeding. They also move tissue out of the way so the surgeon can more easily see what’s happening during a procedure.
Clamps — Clamps are one of the most commonly used tools in surgical procedures. They can block blood flow through an artery or vein to prevent internal bleeding. They also move tissue out of the way so the surgeon can more easily see what’s happening during a procedure. Cotton swabs — Cotton swabs are often used to clean an incision site during or after surgery. If left inside a patient’s body, they also can become infected or interfere with normal bodily functions.
Cotton swabs — Cotton swabs are often used to clean an incision site during or after surgery. If left inside a patient’s body, they also can become infected or interfere with normal bodily functions. Gauze pads — Gauze pads are another tool to clean an incision site during or after surgery. Medical professionals also use them to soak up blood or fluids during the procedure. Gauze left after surgery can quickly become infected, leading to additional complications.
Gauze pads — Gauze pads are another tool to clean an incision site during or after surgery. Medical professionals also use them to soak up blood or fluids during the procedure. Gauze left after surgery can quickly become infected, leading to additional complications. Sponges — Surgical sponges are another implement used to clean incision sites and soak bodily fluids. Like cotton swabs and gauze pads, sponges left inside a patient can become infected.
Sponges — Surgical sponges are another implement used to clean incision sites and soak bodily fluids. Like cotton swabs and gauze pads, sponges left inside a patient can become infected. Needles — Needles used to place sutures inside a surgical patient are some of the most dangerous implements left inside the body. These needles can puncture organs and other tissues because they are sharp, causing severe internal bleeding and other complications.
Needles — Needles used to place sutures inside a surgical patient are some of the most dangerous implements left inside the body. These needles can puncture organs and other tissues because they are sharp, causing severe internal bleeding and other complications. Scissors — Surgical scissors are another of the most dangerous objects that might be left inside a surgical patient. Scissors are much bigger than needles and have multiple sharp edges, which can cause even more damage.
Scissors — Surgical scissors are another of the most dangerous objects that might be left inside a surgical patient. Scissors are much bigger than needles and have multiple sharp edges, which can cause even more damage. Catheters — Catheters are thin, flexible tubes used to either drain fluid from your body or add fluid to it. A catheter left inside a surgical patient can significantly interfere with the patient’s bodily functions or become infected.
Catheters — Catheters are thin, flexible tubes used to either drain fluid from your body or add fluid to it. A catheter left inside a surgical patient can significantly interfere with the patient’s bodily functions or become infected.